Here's why I never trust a single provider with my digital life, and how you can build a bulletproof backup strategy that actually works when disaster strikes.
TLDR; AWS deleted my 10-year account and all data without warning
https://www.seuros.com/blog/aws-deleted-my-10-year-account-without-warning/

Ten years of customer data, code repositories, and business-critical applications vanished overnight. AWS had suspended his account without warning, and his single-provider backup strategy crumbled like a house of cards. This isn't just another horror story—it's a wake-up call that even the most reliable cloud giants can fail you when you need them most. Here's why I never trust a single provider with my digital life, and how you can build a bulletproof backup strategy that actually works when disaster strikes.
1. When Cloud Giants Fail You
Cloud providers market themselves as infallible, but the truth is more unsettling than most realize.
Last month, a developer with a decade-long AWS relationship watched his entire digital empire disappear overnight. His account was suspended due to a billing dispute that escalated through automated systems, with no human intervention until it was too late. The suspension triggered a cascading failure that made his carefully planned backups completely inaccessible—they were all stored within the same AWS ecosystem that had just locked him out.
This scenario plays out more frequently than cloud providers advertise. Enterprise-grade infrastructure doesn't mean failure-proof operations, especially when billing issues or policy violations can trigger account-level suspensions. Uptime monitoring becomes meaningless when your entire cloud presence vanishes with a single administrative decision.
The hidden risk isn't just technical failure—it's systemic dependency. When your primary cloud provider, backup storage, and disaster recovery systems all exist within the same corporate umbrella, you're betting your business on a single point of failure that extends far beyond hardware issues.
2. The Four Pillars of Bulletproof Backup Strategy
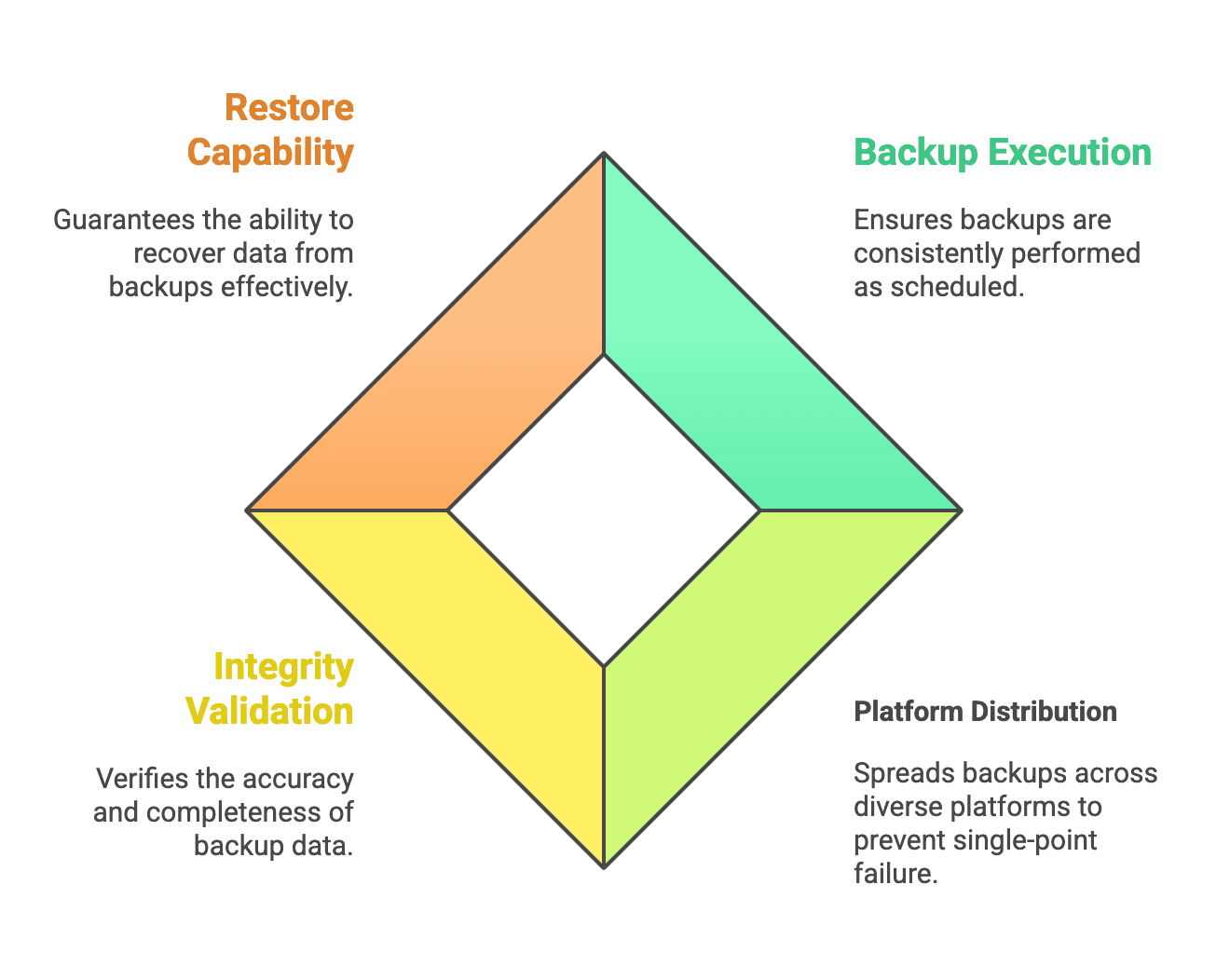
Building resilient backup systems requires more than copying files to cloud storage—it demands systematic monitoring and validation across every component.
First Pillar: Ensure Your Backups Actually Run
Silent backup failures are the invisible killers of data protection strategies. Your backup scripts might complete successfully while actually backing up corrupted data, empty directories, or failing to capture critical database transactions. Heartbeat monitoring transforms backup uncertainty into verifiable assurance by confirming not just that backup processes started, but that they completed successfully with expected data volumes.
Heartbeat monitoring works by requiring your backup processes to check in at predetermined intervals. If a backup job fails silently or hangs indefinitely, the missing heartbeat immediately triggers alerts before you discover the problem during an emergency restore. This approach catches issues like insufficient storage space, network timeouts, or corrupted backup archives that traditional logging might miss.
Pro tip: Set up backup validation scripts that verify file counts, sizes, and checksums after each backup operation, then send heartbeat confirmations only after successful validation.
Second Pillar: Distribute Across Separated Platforms
The three-provider strategy distributes risk across completely independent platforms: your primary provider for daily operations, a secondary provider for frequent backups, and an emergency provider for catastrophic failure scenarios. This approach ensures that account suspension, regional outages, or provider-specific issues can't compromise your entire backup ecosystem simultaneously.
Cross-provider backup implementation requires careful orchestration of sync operations that maintain data consistency across platforms. Multi cloud backup strategies often involve staging data in intermediate locations, managing different API authentication systems, and coordinating backup schedules to minimize bandwidth costs while maximizing data protection coverage.
Key takeaway: Large backups requiring days to restore need incremental recovery strategies—test restore times regularly and implement differential backups or database replication for critical systems that can't wait for full restoration.
Third Pillar: Validate Backup Integrity
Backup completion confirmations provide false security if the underlying data is corrupted or incomplete. Backup monitoring must extend beyond job completion to verify actual data integrity through automated validation processes that detect corruption before you discover it during emergency restore operations.
Effective integrity validation involves more than file size checks. Modern backup systems should verify database transaction logs, test random file samples for corruption, and confirm that backup archives can actually be extracted successfully. Multi cloud backup health checks with 20-second intervals provide rapid detection of integrity issues across different provider platforms.
Data corruption can occur during transmission, storage, or retrieval phases of backup operations. Network interruptions might create partially transferred files that appear complete but contain corrupted segments. Storage system failures could introduce bit rot that gradually corrupts archived data over time. Validation systems must test not just backup creation, but also backup retrieval and restoration capabilities.
Pro tip: Implement automated restore tests that randomly select backup files and verify their contents against checksums or database integrity checks.
Fourth Pillar: Guarantee Restore Capability
The ultimate test of any backup strategy isn't successful data copying—it's successful data restoration when you actually need it. Disaster recovery monitoring validates that your backup systems can perform under pressure, with realistic Recovery Time Objectives (RTO) that account for real-world emergency conditions rather than ideal testing scenarios.
Regular automated restore tests simulate actual disaster scenarios by attempting to recreate production environments from backup data. These tests reveal hidden dependencies, missing configuration files, or backup gaps that only become apparent when you're trying to rebuild systems from scratch. The process often uncovers issues like hardcoded database connections, missing environment variables, or application dependencies that weren't included in backup procedures.
Key takeaway: Backup systems that can't reliably restore data are expensive storage solutions masquerading as disaster recovery—test your restore capabilities regularly and measure actual recovery times.
3. Building Your Resilient Backup Defense Based on Four-Pillar Approach
Transform the four-pillar strategy into actionable steps that build comprehensive backup resilience systematically.
Step-by-Step Implementation Guide
| Step | Action | Key Activity | Success Criteria |
|---|---|---|---|
| Step 1 | Audit Your Current Backup Reality | Document all backup processes and identify single points of failure | Complete backup inventory with failure points mapped |
| Step 2 | Implement Heartbeat Monitoring | Configure backup scripts to send success confirmations to uptime monitoring systems | Heartbeat monitoring active and tested for critical backups |
| Step 3 | Establish Secondary Provider Storage | Configure automated sync to independent secondary cloud provider | Multi cloud backup verification working across providers |
| Step 4 | Build Automated Integrity Validation | Develop validation scripts with backup monitoring alerts for failures | Integrity validation running automatically after each backup |
| Step 5 | Implement Regular Restore Testing | Schedule automated restore tests with disaster recovery monitoring | Weekly restore tests completing successfully with documented procedures |
Key takeaway: Data is always the most critical part to protect in a system
Getting Started with Backup Monitoring
Modern heartbeat monitoring solutions eliminate the complexity of building custom backup verification systems. Start by implementing heartbeat confirmations for your most critical backup processes, then expand coverage to include all data protection operations.
Cloud redundancy monitoring implementation begins with identifying single points of failure in your current backup architecture. Map dependencies between backup processes, storage locations, and recovery procedures to reveal vulnerable connections that could compromise entire protection strategies. This analysis guides prioritization of monitoring investments and redundancy improvements.
Begin building bulletproof backups today by implementing heartbeat monitoring for your next scheduled backup operation. Test the system by deliberately introducing a backup failure and verifying that monitoring alerts trigger as expected. This hands-on experience provides immediate feedback about monitoring effectiveness and reveals opportunities for improvement.
Key takeaway: The best time to implement comprehensive backup monitoring was yesterday—the second best time is right now, before the disaster happens!
Start now to monitor your backup with Bubobot's heartbeat monitoring https://bubobot.com/pricing
Also, check our documentation to know how to create Heartbeat monitoring https://docs.bubobot.com/monitor-types/heartbeat-missed



